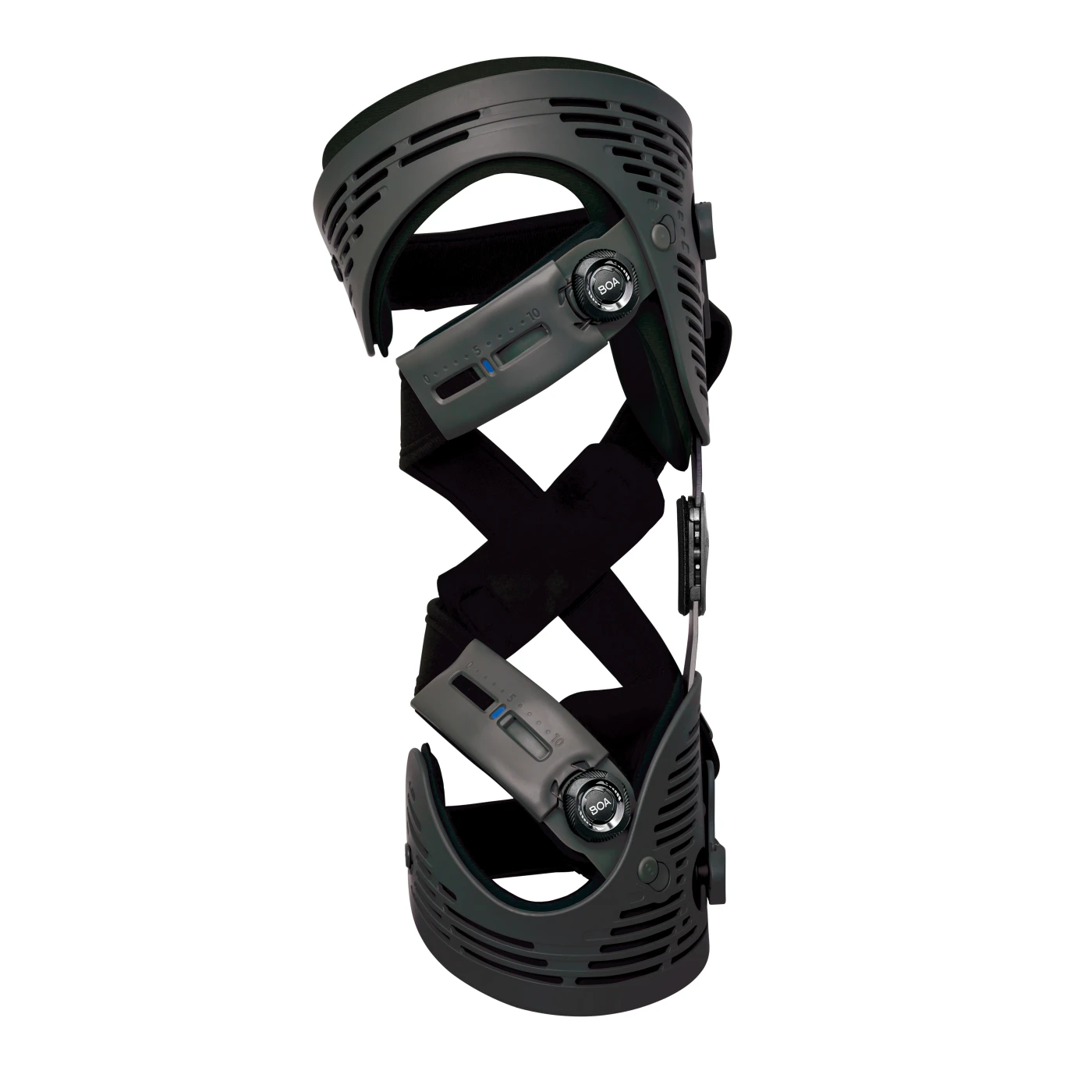
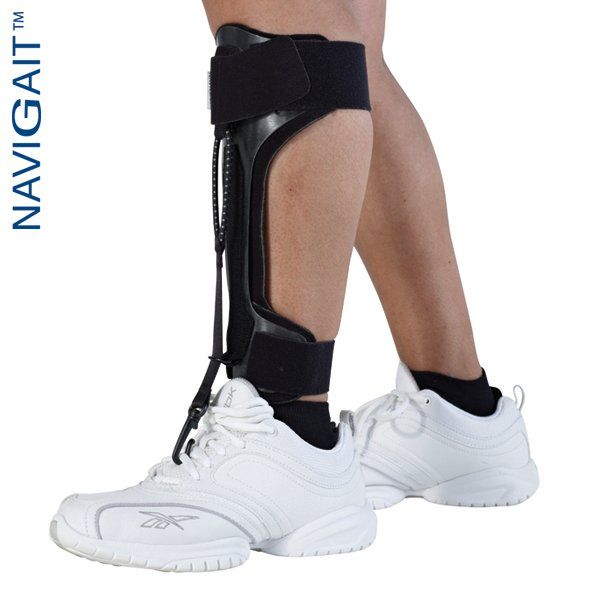
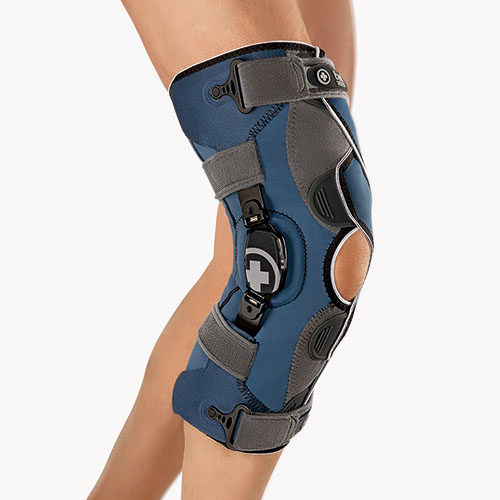
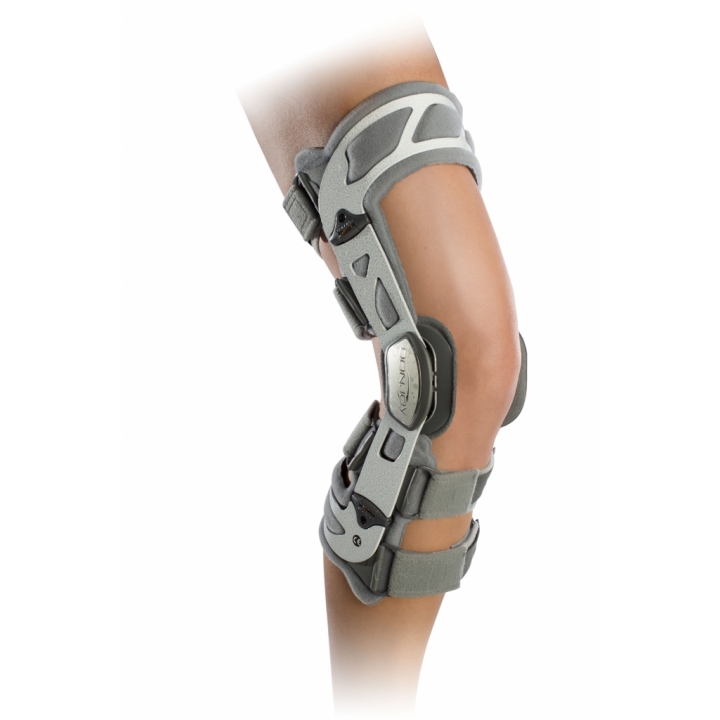
SafetyStride® W/ Y Stirrup and GX
SafetyStride® W/ Y Stirrup and GX
The SafetyStride® is a mechanical stance control orthotic knee joint that utilizes a low-profile cabling system to automatically unlock itself at the end of stance phase. The key feature of the SafetyStride® is its ability to resist knee flexion at any angle. The SafetyStride® does not require full 180° knee extension to resist knee flexion in stance phase.
Knee Joint Selection Guide
Discretion in choosing a joint size and designing an appropriate orthosis should be used by the orthotist in all cases. We would reference and support the approach described by Lunsford and agree that successful orthotic management requires a clear understanding of the condition being treated and a realistic plan to address the biomechanical deficits presented.
For optimal orthotic management, the mechicanical demands to be placed upon the orthosis for any given treatment must be understood prior to material selection.
The selection of the correct materials is often the difference between success and failure and we believe that the orthotist is trained and the best qualified to match the characteristics of the material to the biomechanical and functional needs of the patient.
Discretion in choosing a joint size, selecting the Side Bar Material, and designing an appropriate orthosis should be used by the orthotist in all cases. The following factors are commonly used by orthotists to help determine the level of Biomechanical Deficit. Practical issues including compliance, occupation, environment and social factors should also be taken into consideration.
Biomechanical Deficit Factors
- Single or multiple plane involvement.
- Mobile or fixed deformity.
- Single or multiple segment involvement.
- Presence and magnitude of joint contracture.
- Muscle strength/weakness.
- Presence/extent of spasticity.
- Range-of-motion.
- Proprioceptive and cognitive skills.
- Skeletal and/or joint alignment — malalignment.
- Progressive or non progressive condition.

| Biomechanical Deficit | Mild | Moderate | Severe | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activity Level | Low | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate | High | |||||||||||||||||||
|
Patients Weight LBS (kg) |
80-140 (36-64) |
140-210 (64-95) |
210-320 (95-145) |
80-140 (36-64) |
140-210 (64-95) |
210-320 (95-145) |
80-140 (36-64) |
140-210 (64-95) |
210-320 (95-145) |
80-140 (36-64) |
140-210 (64-95) |
210-320 (95-145) |
80-140 (36-64) |
140-210 (64-95) |
210-320 (95-145) |
80-140 (36-64) |
140-210 (64-95) |
210-320 (95-145) |
80-140 (36-64) |
140-210 (64-95) |
210-320 (95-145) |
80-140 (36-64) |
140-210 (64-95) |
210-320 (95-145) |
80-140 (36-64) |
140-210 (64-95) |
210-320 (95-145) |
|
| 1001 | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | A | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | |
| 1002 | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | A** | B/A | A | A** | B/A | A** | — | |
| 1003 | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | A | — | — | A | — | — | |
| 1004 | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | A | A | — | A | — | — | |
| 1006* | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | A | A | — | — | — | — | |
| 1007* | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | A | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 1010* | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | A | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 1012 | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | — | — | — | |
| 1013* | — | A | — | — | A | — | A | A | — | — | A | — | — | A | — | A | A | — | A | A | — | A | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 1015 | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | A | A | A | — | — | — | — | |
| 1017 | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | A | A | — | |
| 1017-A38* | — | — | A | — | — | A | — | — | A | — | — | A | — | — | A | — | — | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | |
| 2004* | B | B | — | B | B | — | — | — | — | B | B | — | B | B | — | — | — | — | B | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 2009* | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | A | A | — | A | — | — | |
| S2001* | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | A | A | — | A | — | — | |
| S2003* | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B | A | — | B | A | — | B/A | A | — | B/A | A | — | A | A | — | A | — | — | |
Steel and Aluminum Alloys
Steel is stronger and stiffer than aluminum allow; aluminum allow has a lower density making it lighter. Steel is fatigure resistant and combines high rigidity, or ductility depending on the alloy. The main disadvantage of steel is its weight. The major benefit of aluminum in orthotics is its high strength to weight ratio. Aluminum does however have a lower endurance limit under repreated dynamic loading conditions than does steel. A common clinical question relates to the upright of a lower extremity orthosis in which deformation under bending stresses is very important. In general terms, if loading conditions are known to be great or highly repetitive, steel is superior to aluminum.
Considerations for Preventing Failure:
- Fatigue.
- Bend Radii.
- Stress Concentration.
- Design.
- Finishing.